
10 Secure Ways to Store Your Business and Consumer Data in the Cloud
Table of Contents
We are seeing cloud storage becoming a more popular deployment choice among companies. The cloud’s portability and simplicity of access make it one of the handiest options.
Companies that use the cloud, on the other hand, maybe more vulnerable to security risks and hackers.
Data breaches revealed 4.1 billion records in the first and second quarters of 2019, demonstrating the magnitude of the problem in the world today. It even increased dramatically during the pandemic with more remote employees working from home.
According to Central, the most common methods for data to be compromised include weak or stolen credentials, back doors, malware, social engineering, having too many rights, insider threats, and poor setup or user mistake. The majority of assaults are aimed at stealing money, although some are also aimed at spying.
Businesses in the new normal necessitate enforcing better and more robust data intake, sharing, and storage protection. You need to get secure cloud storage to prevent putting your data in danger. Procedures must be in place to eliminate these vulnerabilities and safeguard your important data.
Here are the best methods for keeping your data safe on the cloud:
Top 10 Ways of Securing Cloud Data in 2021
1. Remember that you are perpetually a Target
 Never think that it will never happen to you or your company. The simplest way to become vulnerable to cyber-attacks is to get complacent. Nearly half of all cyber-attacks are focused on small businesses, assuming that they have not taken appropriate data security safeguards.
Never think that it will never happen to you or your company. The simplest way to become vulnerable to cyber-attacks is to get complacent. Nearly half of all cyber-attacks are focused on small businesses, assuming that they have not taken appropriate data security safeguards.
Smaller businesses, on the other hand, have fewer resources than larger organizations. Therefore, they usually cross their fingers and hope for the best. Whether it sells in-person or exclusively through e-commerce, every small business should invest in customer and data protection. When it comes to cybersecurity, you can never be too vigilant and you can find more information about it on the British National Cyber Security Centre Website. Prudence and reasonable scepticism will get you a long way.
2. Select a Cloud Provider with Caution

Any external cloud provider on your shortlist should come highly recommended by peers, be authorized by respected, experienced businesses, and be well-versed in your industry. Seek a tailored strategy rather than a one-size-fits-all solution, and keep in mind that your needs and volume may change over time. Start-ups should be rigorously scrutinized. Not all start-ups can continue to achieve the desired results as they develop.
3. Configure Backup and Recovery Options

Even though the technology is becoming increasingly sophisticated, there is still the possibility of experiencing technological issues or even user errors. That is why it’s essential to back up your data. The loss of data on which your organization depends can result in significant disruption and financial loss, not to mention disgruntled customers.
Most systems now allow you to save several versions of your database, allowing you to recover data from specified periods and guaranteeing that you never lose data in the case of a system crash or inadvertent deletion. You will never have to worry about losing critical information to the success of your organization if you back up your data.
4. Use Data Encryption

Encrypt sensitive data stored on servers or removable media for sharing with business partners by implementing complete disk protection.
Encryption, or converting data into secret codes, prevents hackers from gaining access to your cloud data. Because encryption transforms your data into ciphertext, hackers must work much more complicated and spend far more time decoding what they are reading.
Only hackers with advanced cryptography skills would be able to decipher the codes in your database with this in place. Data encryption will add an extra layer of security to your data, keeping it safe from hackers and other threats.
5. Use more secure Passwords

In general, computer systems are secure. Human behavior is typically the root cause of the most severe IT risks. Allowing employees to share logins or use basic, traditional passwords undermines one of the most critical lines of protection against hackers or criminals who have gained unauthorized access to your computer equipment. Your IT staff implements and regularly must audit a password policy to ensure that users update their passwords regularly and do not use shared or generic passwords.
When users remember several passwords for different systems, a password management solution such as “1password” or “Keypass” is usually beneficial. Password management software allows users to preserve login credentials in encrypted files, which may then be recovered as needed. Your IT administrators will be able to enforce password restrictions such as frequent updates and unique character sequences by using analogous techniques.
6. Configure User Permissions
Not every employee in your organization needs access to every piece of data you have. Make sure that user permissions are configured in line with your organizational structure. This guidance is designed to keep inexperienced personnel from making unintentional changes to critical databases. Although it appears to be a no-brainer, many firms have made the mistake of having too many or unorganized licenses, which eventually leads to problems.
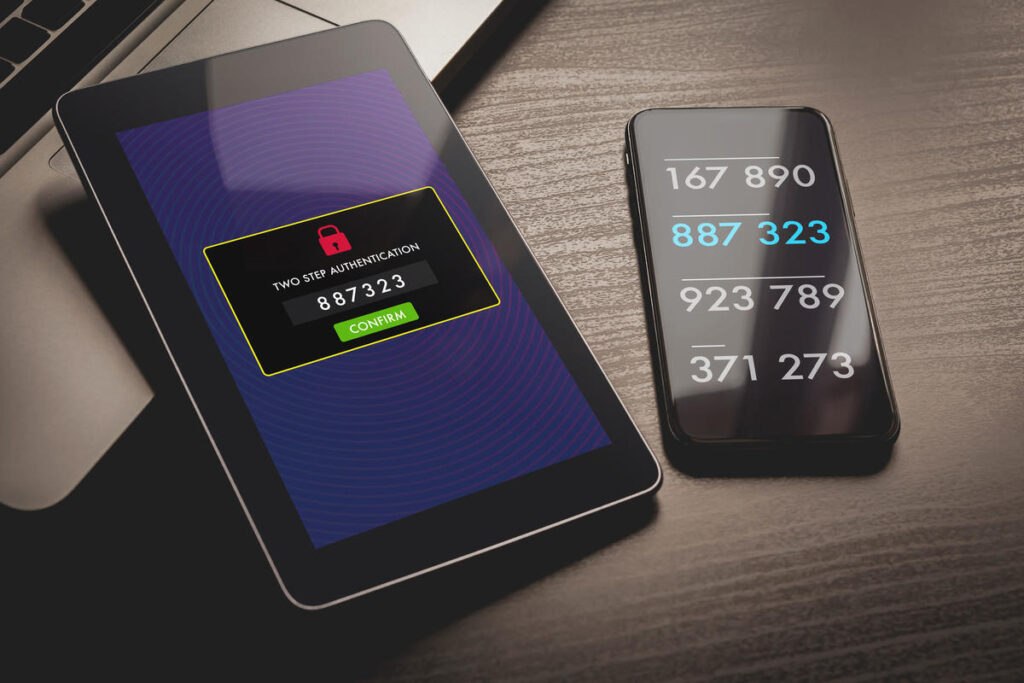
7. Set up a Device Control Strategy and 2FA

You need a system to detect and regulate the usage of portable storage devices — this not only prevents bad material from coming in, but it may also help block personally identifiable information (PII) and intellectual property (IP) data from leaving.
It is critical to safeguard your systems and the devices through which you access those systems. It is a straightforward method for removing insider risks. Install a firewall solution on your network. A virtual private network is another option to safeguard your gadgets (VPN). While connecting to public internet services, a VPN creates a private network. It offers internet privacy as well as encrypted and secure connections to protect the safety of your data.
Also, enforce 2FA (two-factor authentication) to enhance personal security. With this approach, your safety is doubled by adding one extra step for each login method you use. It forces those seeking sensitive data access to enter their password in addition to a single-use security code sent to their device before permitting secure login.
8. Secure Data Transfers
 Maintain point-to-point security by requiring further encryption and using SSL for all connections. You can track and manage who sees communications about your data, how long they have access, and when and how access may be cancelled using secure email and file protection technologies (for all actions or specific tasks such as forwarding).
Maintain point-to-point security by requiring further encryption and using SSL for all connections. You can track and manage who sees communications about your data, how long they have access, and when and how access may be cancelled using secure email and file protection technologies (for all actions or specific tasks such as forwarding).
You can restrict the sorts of data transmitted outside your business. Limit the permissible use of data and verify that you and the receiver comply with all applicable data protection regulations.
Uploading sensitive information should be avoided. Of all, the whole idea of the cloud is to have access to all of your data in one place. However, ensure that your personal information, identifying information, and sensitive information are disposed of in the event of a probable breach in advance. Furthermore, ensure that no files include your passwords or other login credentials, which would allow a hacker to access the remainder of your data quickly.
9. Run Tests and Background Checks

Most essentially, after you’ve taken these steps, you should conduct security system tests. Analysing your company’s performance about your security setup may reveal where adjustments are required. You may also engage an outside team of hackers to test the security of your systems to ensure the safety of our customers and data. Keeping your system in the cloud implies that it will very certainly require continuous maintenance or updates, and testing should be performed to ensure that your defensive system is working correctly.
You should also perform background checks regularly. Be very cautious when recruiting new staff; protecting against internal risks is critical to successful cybersecurity. Investigate their past to get a sense of the type of person they are. Additionally, keep an eye out for changes in the personality of current employees since this might be an indication of additional problems.
10. Defend against Malware
 Protect your data by protecting your PCs and network against viruses. Malicious software capable of causing vast quantities of data harm, malware can swarm on vulnerable devices without your knowledge.
Protect your data by protecting your PCs and network against viruses. Malicious software capable of causing vast quantities of data harm, malware can swarm on vulnerable devices without your knowledge.
You must safeguard yourself from viruses by doing the following:
- Install the firewall: While not sufficient on its own, your router’s onboard firewall serves as the initial line of defense, therefore enable it.
- PC security: Advanced security software protects without interfering with the functionality of your machine or network. Look for security that can handle identity theft, suspicious websites, and hackers all at once.
- Keep your emails clean: Anti-spam software safeguards against unsolicited communications, which can pose dangers and distract staff. With the appropriate safeguards, you can stop them in their tracks.
Conclusion: Educate Your Employees and Remote Workers
Everyone in your organization must understand the company’s security policy and business leaders need to educate remote workers on this important aspect of their work. Whether you want to do it during onboarding or do bi-annual refresher sessions, it is worthwhile to do so – just make sure everyone adheres to the principles across the board.
All workers (especially those with access to private information) should undergo data security training. The dangers and repercussions of a data breach should be thoroughly discussed, as should recommendations for device usage, data access procedures, password selection, and two-step authentication. Make the consequences for workers who are found to be the cause of a violation apparent – from termination to criminal prosecution.
Cloud services have quickly surpassed traditional methods of onsite company data storage as a primary alternative. While cloud data storage has several advantages, including cost savings and ease, any advantages can be rapidly lost if the data is exposed. Having adequate security measures for safeguarding and securing your data in the cloud should be discussed well before a move to the cloud occurs.
No company is safe from cybercrime. However, if you use the most potent and diverse techniques to repel prospective invasions, you are more likely to deter such efforts and limit any harm that may occur. For instance, remote working with Microsoft tools and its touchless solutions like servers and cloud storage can be fully maximized if you educate your team with best practices and the know-how to use the tools for optimum collaboration.
Author Profile
- Mayleen Meñez worked as a writer, graphic artist and video editor for 8 years before finding her passion as a teacher and missionary in a faith-based NGO, serving in the Philippines and Asia. She currently serves in an international ministry, homeschools 3 kids, and loves cooking in her spare time. She is also a resident SEO writer for Softvire. Follow her at mayleenmenez.

